
In today’s connected world, IT (computers and networks) and OT (machines and control systems) are coming together. But what about OT Security? This mix brings lots of new benefits, like better efficiency, but also creates new security risks that need careful handling to keep everything safe and running smoothly.
We’re exploring the smaller, or finer details and distinctions of OT security, focusing on IT and OT security, and the impact of IoT on OT systems.
Understanding OT Security
Operational Technology (OT) includes hardware and software that detects or causes changes through direct monitoring and control of physical devices, processes, and events in enterprise environments.
Common in industries such as manufacturing, energy, and transportation, OT systems include SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), and DCS (Distributed Control Systems).
Unlike IT systems, which manage data and communications, OT systems control physical processes. The primary concern in OT security is ensuring the reliability and safety of these processes. Any compromise can lead to severe consequences, including production halts, safety hazards, and significant financial losses.
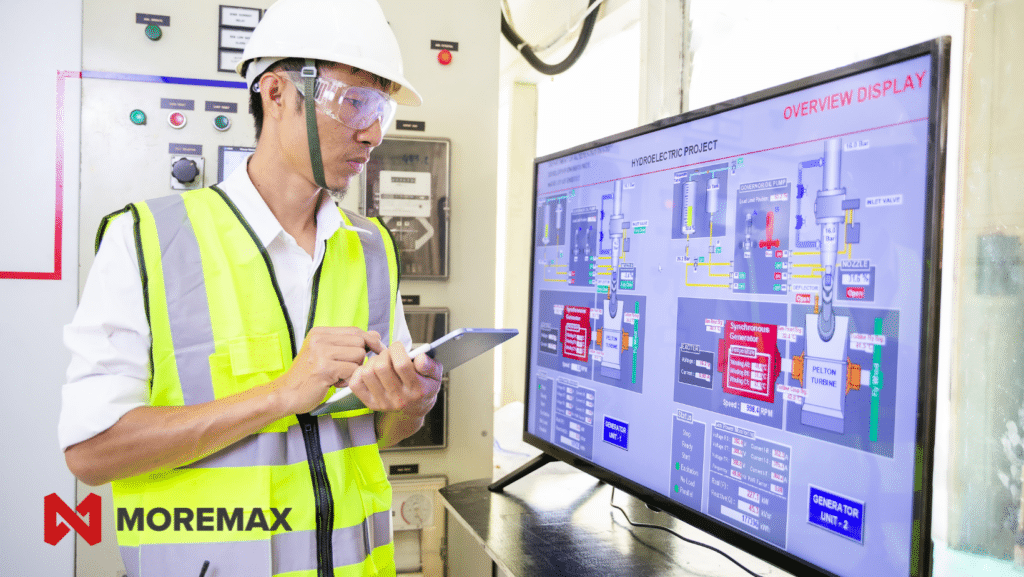
The Combination of IT and OT
The line between IT and OT is blurring. This combo is driven by the need for improved efficiency, real-time analytics, and enhanced decision-making capabilities. However, this integration also introduces vulnerabilities. Traditional IT security measures are not always adequate for OT environments due to their unique requirements.
Challenges in IT and OT Security Convergence:
- Legacy Systems: Many OT systems were designed decades ago with little consideration for security. Integrating these with modern IT systems can expose vulnerabilities.
- Different Priorities: IT systems prioritize data confidentiality and integrity, while OT systems emphasize availability and safety. Balancing these priorities is challenging.
- Complex Networks: OT environments often feature complex, heterogeneous networks that are difficult to secure and monitor.
The Role of IoT in OT Security
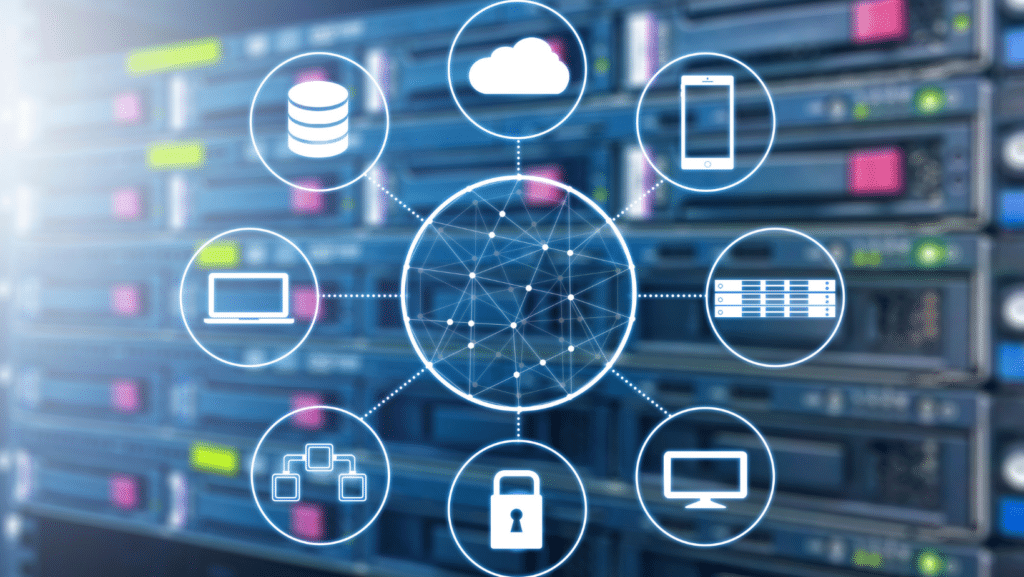

The rise of the Internet of Things (IoT) has transformed OT environments. IoT devices collect and transmit data, enabling real-time monitoring and control. However, these devices can be a double-edged sword. While they offer numerous benefits, they also expand the attack surface.
Key Security Concerns with IoT in OT:
- Increased Attack Surface: Each IoT device connected to an OT network can be a potential entry point for cyber threats.
- Device Management: IoT devices often lack robust security features and may not receive regular updates, making them vulnerable to attacks.
- Data Security: The vast amount of data generated by IoT devices needs to be securely transmitted and stored to prevent unauthorized access.
Best Practices for OT Security
Securing OT environments, especially with the integration of IT and IoT, requires a comprehensive approach. Here are some best practices to enhance OT security:
- Network Segmentation: Divide the network into smaller segments to limit the spread of an attack. Critical systems should be isolated from less secure parts of the network.
- Regular Audits: Conduct regular security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and address potential weaknesses.
- Patch Management: Ensure all systems, including legacy OT devices and IoT devices, are regularly updated with the latest security patches.
- Access Control: Implement strict access control measures. Only authorized personnel should have access to critical systems.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploy IDS to monitor network traffic for suspicious activity and respond promptly to potential threats.
- Employee Training: Educate employees about cybersecurity best practices. Awareness and training can significantly reduce the risk of human error leading to security breaches.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to quickly address and mitigate the impact of security incidents.
Future Trends in OT Security

As technology continues to evolve, so too will the landscape of OT security. Here are some emerging trends to watch:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): AI and ML can enhance threat detection and response capabilities by identifying patterns and anomalies that may indicate security breaches.
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain can provide secure and immutable records of transactions and processes, enhancing the integrity and traceability of OT systems.
- 5G Technology: The rollout of 5G networks will enable faster and more reliable connectivity for IoT devices in OT environments, but it will also require new security measures to address the increased connectivity.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Adopting a zero-trust approach, where no entity is trusted by default, can help protect OT environments by requiring continuous verification for access to resources.
Conclusion
The combination of IT, OT, and IoT offers significant benefits for industrial operations, but it also introduces new security challenges. Understanding the unique aspects of OT security and implementing robust security measures is crucial for protecting critical infrastructure and ensuring operational continuity.
By staying informed about emerging trends and best practices, organizations can effectively navigate the complexities of IT and OT security in an increasingly connected world.
WE’D LOVE TO CHAT ABOUT HOW WE CAN HELP!



Related Posts