
Email remains a cornerstone of communication for businesses worldwide. However, with the rise of cyber threats, ensuring the security of your email communications is paramount. One powerful tool in email security is DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance). We’ll be discussing what DMARC is, why it’s important, and how implementing it can bolster your business’s security and efficiency.
What is DMARC?
DMARC is an email authentication protocol that helps protect your organization’s email domain from being used for email fraud, phishing, and other malicious activities. It works by allowing senders to specify how they want emails from their domain to be handled if they fail authentication checks.
Why is DMARC Important?
Starting in February 2024, new rules were made for businesses sending over 5,000 emails daily to Google and Yahoo! accounts. These rules said they must use an active DMARC policy. This helps make email safer by reducing phishing, spam, and cyber fraud risks. According to a report by Egress, in 2022, 92% of organizations were victims of phishing attacks.
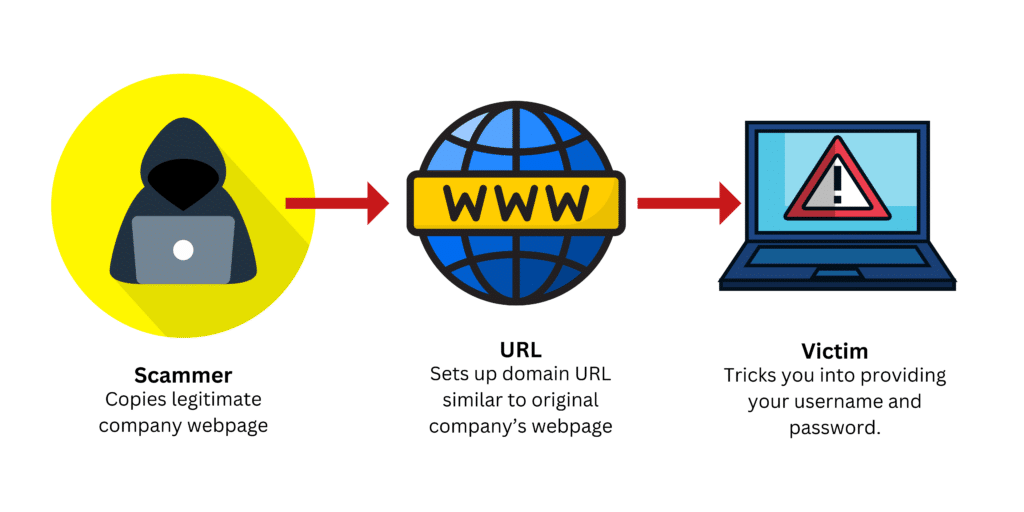
Email phishing attacks are becoming increasingly sophisticated, making it challenging for traditional email filters to detect them. DMARC helps combat these threats by providing a standardized way for email receivers to verify the authenticity of incoming messages. By implementing DMARC, you can:
- Prevent Email Spoofing: DMARC helps prevent cybercriminals from spoofing your domain to send fraudulent emails, thereby protecting your brand reputation and maintaining customer trust.
- Reduce Phishing Attacks: Phishing attacks, where attackers impersonate legitimate entities to deceive recipients into disclosing sensitive information, can be mitigated through DMARC’s authentication mechanisms.
- Enhance Email Deliverability: By setting DMARC policies, you can instruct email providers on how to handle messages that fail authentication, reducing the likelihood of legitimate emails being marked as spam or not delivered at all.
- Gain Visibility: DMARC provides valuable insights into who is sending emails on behalf of your domain, allowing you to identify unauthorized senders and take appropriate action.
How Does DMARC Work?
DMARC operates alongside two other email authentication protocols: SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail). Here’s how they work together:
- SPF: SPF allows domain owners to specify which IP addresses are authorized to send emails on behalf of their domain. When an email is received, the recipient’s mail server checks if the sending IP is listed in the domain’s SPF record.
- DKIM: DKIM adds a digital signature to each outgoing email, verifying that it originated from the claimed sender and that the message content has not been altered in transit. The recipient’s mail server validates this signature against the sender’s public key published in their DNS records.
- DMARC: DMARC builds upon SPF and DKIM by enabling domain owners to specify how their emails should be handled if they fail authentication. This includes options such as monitoring, quarantining, or rejecting the failed messages.
Setting Up DMARC for Your Business
Now that you understand the importance of DMARC, here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing it for your business:
- Assess Your Current Email Infrastructure: Begin by auditing your existing email infrastructure to identify all authorized senders and any third-party services that send emails on your behalf.
- Initial SPF and DKIM Configuration: Ensure that your domain has SPF and DKIM records configured correctly. This involves listing all authorized sending IP addresses in your SPF record and generating DKIM keys for signing outgoing emails.
- Publish a DMARC Record: Once SPF and DKIM are in place, publish a DMARC record in your DNS settings. This record specifies your DMARC policy and includes instructions for email receivers on how to handle messages that fail authentication.
- Monitor and Analyze DMARC Reports: Enable DMARC reporting to receive feedback on email authentication results. Analyze these reports regularly to identify any issues or unauthorized senders that need to be addressed.
- Gradually Enforce DMARC Policies: Start by setting your DMARC policy to “none” or “monitoring” mode to monitor email authentication without impacting email delivery. Once you’re confident that all legitimate emails are passing authentication checks, gradually tighten your DMARC policy to “quarantine” or “reject” mode.
- Continuously Monitor and Update: Email security threats are constantly evolving, so it’s crucial to stay vigilant and update your DMARC policies and configurations regularly to adapt to new threats and technologies.
Staying Ahead of Cyber Threats
With cyber threats becoming more sophisticated,
Securing your business’s email communications is non-negotiable. DMARC provides a robust framework for authenticating your domain’s emails, protecting against phishing attacks, and maintaining brand integrity. DMARC provides a critical defense mechanism. It empowers organizations to take control of their email security, significantly reducing the likelihood of email-based attacks.
Take the necessary steps today to make your email defenses stronger and keep your business productive and efficient in the face of evolving cyber threats.


Related Posts